Extensions
Since version 5.0.0 SeedDMS has support for customer extensions which allow to modify the behaviour of SeedDMS in various ways. Extensions are all placed below the directory ext with each extension being in their own subdirectory. Shipping an extension is done by zipping the content of such a subdirectory and naming the resulting archive extensionname-x.y.z.zip. This archive may not contain the extension directory itself.
Extension manager
Managing of all extensions is done by Extension manager. The extension manager requires admin rights and is located in the administration of SeedDMS.
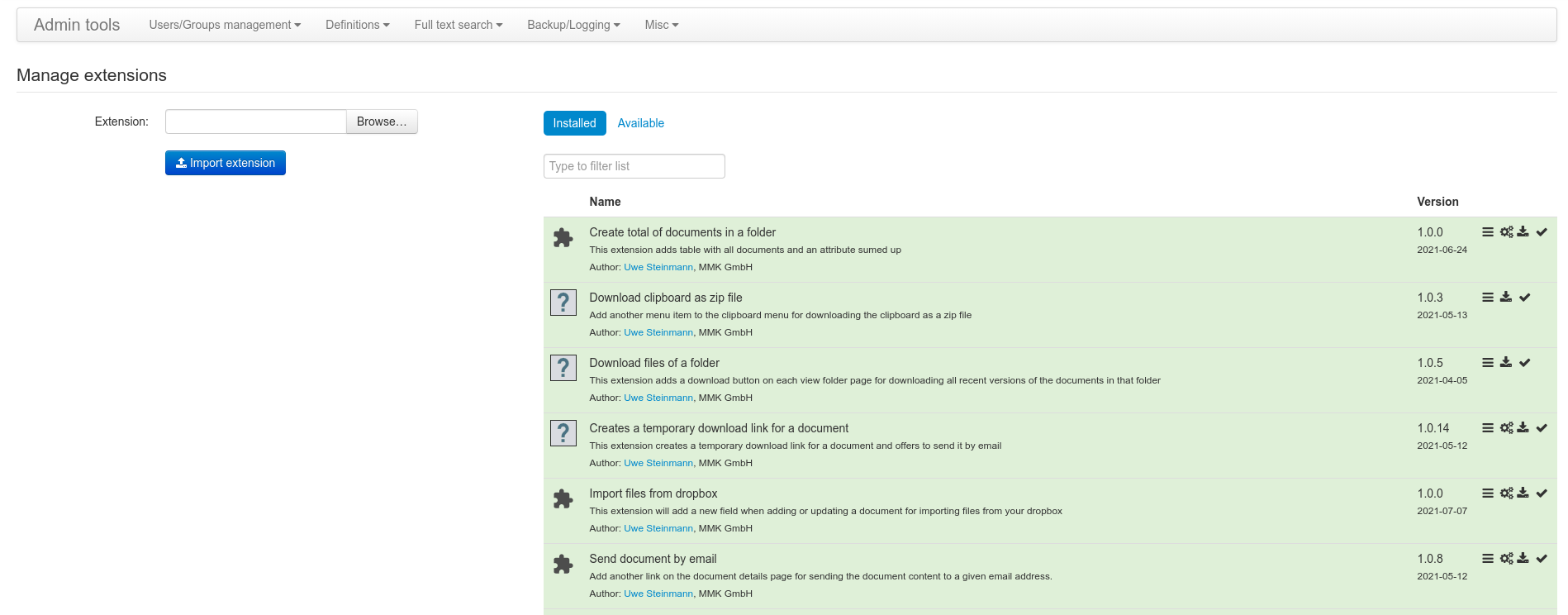
Extension manager
The extension manager can be used
to check compatibility of the each extension with the current version of SeedDMS
to upload an extension
to download an extension
to install an extension from a remote repository
to read the change log of an extension
to enable/disable an extension
There are two tabs within the extension manager. One titled ‘Installed’ and another one titled ‘Available’. The ‘Installed’ tab lists all currently installed extensions. They are marked with different background colors.
green stands for enabled and working extensions
yellow indicates disabled extensions
red marks extension which have been deactived because of a problem, e.g. the extension is incomplete or was created for a different version of SeedDMS.
The ‘Available’ tab will only list extension if a remote repository of extension is configured in the settings of SeedDMS. Extensions are also marked with different background colors.
green stands for installed, enabled and working extensions
white marks extension available in the repository which are not installed yet
Structure of an extension
Each extension must at least contain the following files.
- conf.php
a php file with the main configuration of the extension
- changelog.md
a plain text file using markdown for listing the changes
- icon.png or icon.svg
an icon shown in the extension manager for this extension
Actually the names of changelog.md and icon.png or icon.png are not fixed but commonly used. Their names must match the names specified in conf.php.
Depending on what the extension does, additional files are required. Most likely a file named lang.php containing additional phrases and its translations and a php file containing a class which must extend the SeedDMS_ExtBase class. If the class contains a method init() it will be called on every http request. The class itself is instanciated by passing the current configuration and the logger to its constructor.
The file conf.php contains the central configuration for the plugin.
1<?php
2$EXT_CONF['example'] = array(
3 'title' => 'Example Extension',
4 'description' => 'This sample extension demonstrate the use of various hooks',
5 'disable' => false,
6 'version' => '1.0.1',
7 'releasedate' => '2018-03-21',
8 'author' => array('name'=>'Uwe Steinmann', 'email'=>'uwe@steinmann.cx', 'company'=>'MMK GmbH'),
9 'config' => array(
10 ),
11 'constraints' => array(
12 'depends' => array('php' => '5.6.40-', 'seeddms' => '5.1.0-'),
13 ),
14 'icon' => 'icon.png',
15 'changelog' => 'changelog.md',
16 'class' => array(
17 'file' => 'class.example.php',
18 'name' => 'SeedDMS_ExtExample'
19 ),
20 'language' => array(
21 'file' => 'lang.php',
22 ),
23);
The php code in conf.php fills a global variable $EXT_CONF which contains the configuration of all installed extension.
The most simpliest version of class.example.php looks like the following.
1<?php
2/***************************************************************
3* Copyright notice
4*
5* (c) 2021 Uwe Steinmann <uwe@steinmann.cx>
6* All rights reserved
7*/
8
9/**
10 * Example extension
11 *
12 * @author Uwe Steinmann <uwe@steinmann.cx>
13 * @package SeedDMS
14 * @subpackage example
15 */
16class SeedDMS_ExtExample extends SeedDMS_ExtBase {
17 function init() { /* {{{ */
18 } /* }}} */
19}
The method init() is commonly used for setting up hooks called by SeedDMS from various places.