Scheduler
Since version 6.0.x SeedDMS has a so called Scheduler which is quite similar to the well known cron daemon on unix systems. It actually requires a cron job on the SeedDMS server to do its work (see below on how to set it up). The scheduler can be found in the admin area.
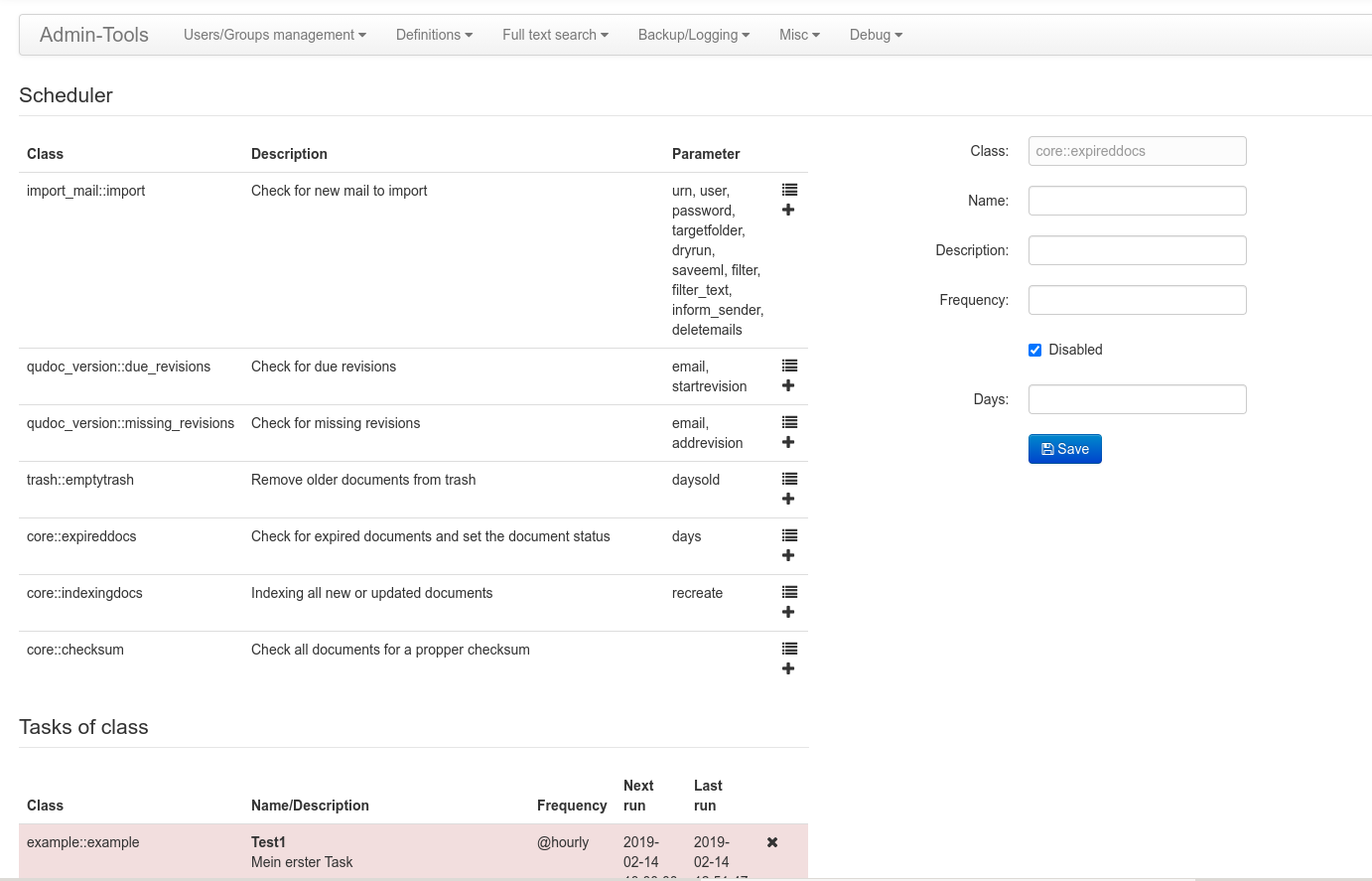
Scheduler
The scheduler runs an arbitrary number of tasks which are set up by the administrator.
The page of the scheduler is divided in three areas. The upper left area list all available task classes. Those with a class name starting with core are shipped with SeedDMS. Other may be added by extensions. A task class is like a blueprint for a task. The list of classes also includes a description and a list of parameters for controlling the behaviour of an instanciated task. The last column of that table has two icons. One for creating a task from this class and one for listing all task already created. The list of created tasks will show up below the list of classes. I new task will be added with the form on the right hand side of the list of classes once the plus button was clicked. It is perfectly fine to have more than one task based on the same task class, e.g. to run an incremental fulltext indexing every hour and a recreation of the fulltext index once a day at night. Each task has a common set of paramters
- Name:
An arbitrary name which allows to easily identify the task.
- Description:
An arbitrary description with additional information on the task.
- Frequency:
A string determine how often this task shall be run. This is identical to the string used to specify the frequency of cron jobs. It consists of five elements as described below.
- Disabled:
A checkbox for disabling this task.
All other parameters are specific to the task class and may vary.
Setting up the scheduler
Running the configured tasks in SeedDMS actually requires to run the scheduler, which than interates over all tasks and starts those which are due. Of course, the scheduler in SeedDMS will not run unless it is itself frequently triggered by calling the shell script utils/seeddms-schedulercli. This is usually done by a cronjob on the SeedDMS Server. seeddms-schedulercli has two command line parameters
- –config:
This is for specifying the path to the configuration file of SeedDMS
- –mode:
This is for setting the mode.
The mode can be one of
- run
for running all task due (this is the regular operation)
- dryrun
similar to run but without running the actual task. For each task ready to run a message is output instead.
- check
does some internal consistency checking of each task class, which are only helpfull when implementing task classes.
- list
for listing all task no matter whether they are ready to run or not. An example output is shown in the figure below.
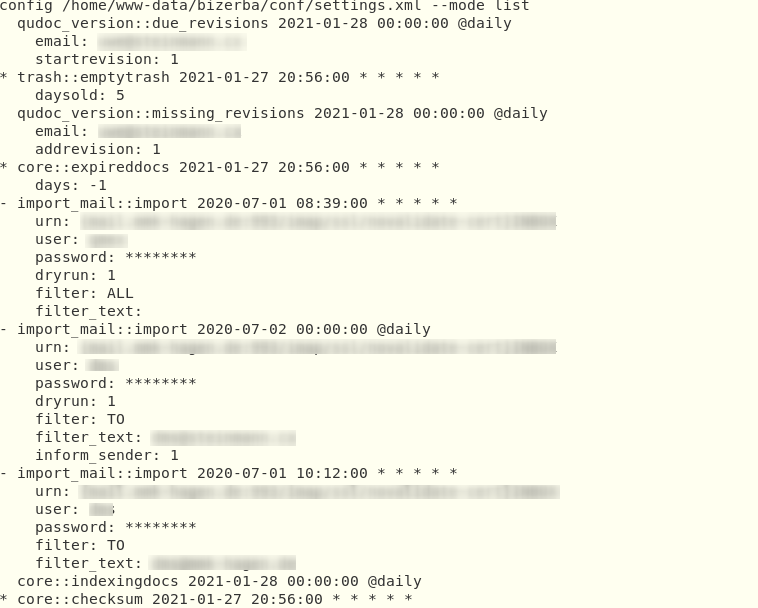
Tasks as listed by the seeddms-schedulercli
Each task in the list starts either with a blank if its enabled but not scheduled for running, a - for tasks currently disabled, or a * for tasks scheduled for running. The first line of each task also list the name of the task class, the date/time of the next scheduled run, and the frequency of this task. All indented lines are parameters, which are specific for this particular task.
All tasks run by the scheduler require a user in SeedDMS named cli_scheduler. Without this user, the script seeddms-schedulercli will quit with an error message.
The script seeddms-schedulercli run be the unix cronjob should always be executed with the same user used by the web server, especially if files on the disc are modified. If the script runs with less privileges it may not be able to do the needed modifications, e.g. creating a new document or removing a document. On the other hand, if it has sufficient privileges but runs as a different user (e.g. root), it may create documents which cannot be modified or deleted by SeedDMS afterwards.
Setting up the cronjob
seeddms-schedulercli checks for due tasks and runs them only if it is called frequently itself. On Unix/Linux system this is done by a cronjob like the following
*/5 * * * * /<path to seeddms>/utils/seeddms-schedulercli –mode=run
It runs the scheduler every 5 minutes. If the script is executed with its complete path, the configuration file will be found without explicitly specifying it on the command line. Add the cron job for the user running the web server.
How often the scheduler script should be run, mostly depends on how frequently the individual tasks are to be run. You should run the cronjob at least as often as your most frequent running task.
For testing purposes you can of course run the cron job command on the command line to ensure it is working propperly.
Built in tasks
SeedDMS ships some task classes already which are listed below with their class name.
- core::expireddocs
This task class checks for expired documents within the last n days. The number of days can be configured when setting up the tasks. There is usually just one task of this class required.
- core::indexingdocs
This task class is a replacement for the already existing script seeddms-indexer for creating or updating the full text index. Whether to recreate or update the index is configured with a task parameter. A possible indexing strategy could be to set up two tasks. One for updating the index more frequently over the day and one for recreating the index at night. Please note that documents which has partly been indexed (just the meta data but without the document contents, because its size exceeded the maximum size for instant indexing) will not be indexed again. There is currently no way to tell if a document was partly of fully indexed. That is why it is important to recreate the index once in while.
- core::checksum
This task class was added in SeedDMS 6.0.15. It checks the checksum of all document versions and reports a mismatch. It also checks if the file of the document version actually exists on disc and issues a warning if not. Use this task to check for modifications of your document content files on disc.
- core::preview
This task class was added in SeedDMS 6.0.16. It checks for missing preview images and creates them if necessary. The main purpose of this task is to defer the creation of preview images because it delays folder listings considerably when many new documents were added or a preview image converter for a certain mimetype was set up the first time affecting lots of existing documents.