Fulltext indexing
Finding a document in SeedDMS can be done either by searching the database or
the fulltext index. The fulltext index is created from meta data of the documents
and their latest document content which is converted into plain text by configurable
conversion programs. The fulltext search is only available to the users
if it is turned on in the settings. SeedDMS only creates or updates the
fulltext index automatically, if the size of the document version does not
exceed the configured files size as specified in the configuration (Maximum
filesize for instant indexing). Though
it always adds some initial meta data of a
new document after it has been uploaded. The fulltext index must be updated
or recreated either manually by the administrator or by a cron job running
utils/indexer.php. There is a practical reason for it. If a users uploads
a large document, it could take several minutes to index the document
content depending on how fast the conversion program runs.
It may even fail because the maximum execution time of a php script is exceeded.
Since version 5.1.21 and 6.0.14 two major changes have been introduced when indexing.
Folders are indexed as well. As there is no content only the metadata of the folder is taken into account.
The index stores the users, who are allowed to read a document or folder.
The second point can result in major speed improvements because the list of found documents and folders may not be checked for sufficient access rights anymore, if the fulltext index is up to date.
Since version 5.1.23 and 6.0.16 another option for updating the fulltext index has been introduced based on the internal scheduler of SeedDMS (see section `Scheduler`_). The task core::indexingdocs can be used for both recreating the whole index or updating it.
Which documents are indexed?
Basically, SeedDMS can index any document type as long as there is a piece of software that converts the content into a plain text. The command to be executed in this conversion process must be configured in the settings per mime type. The command expects a filename and must output the text to stdout. The command may use a placeholder %s which is replaced by the filename. The most simple example on Unix/Linux systems for converting plain text files is cat %s. This rather generic way allows to add documents without textual information to the fulltext engine by use of OCR software or even speech recognition software.
SeedDMS has support for two different kinds of fulltext index.
The older one is based on lucene and is provided by the Zend Framework
The newer one is based on sqlite
The one to be used must be configured in the settings. While the lucene based indexing is quite mature and stable it is also quite slow when indexing documents. The sqlite based indexing is available since version 4.3.20 and is much faster and therefore recommended.
Indexing
Full text indexing is only available if it is turned on in the configuration (Enable Full text search).
The indexing of documents covers two parts
the document’s meta data and
the documnet’s content.
The indexing of folders just covers the meta data.
When a document is uploaded only its meta data is indexed by default. The indexing of the content must be done later, either by running the indexer as a cron job or in the admin tools by starting it manually. Consequently, a document can be found after upload only by its meta data. This behaviour can be changed by setting the configuration variable ‘Maximum filesize for instant indexing’. Documents with a size below this integer value will also be indexed by content right after upload. Keep in mind, that indexing large documents may take some time which will delay the upload process. Setting this configuration variable to 0 turns off the instant indexing of the document content.
When a document is deleted it will also be removed from the fulltext engine. Updating a document or removing the latest version will reindex the latest version of the document.
The management of the full index itself is done by three function in the admin tools
Create fulltext index
Update fulltext index
Fulltext index info
Creating a fulltext index will remove an existing one and indexes all documents/folders again. This may take some time and should not be necessary unless you change the fulltext engine or want to make sure that your fulltext index is in any case up to date. The indexing will always only read the latest version of a document. Previous versions will not be indexed.
Once you start indexing documents, you will see a page with a hierachical list of all documents and two progress bars on top of that page. The list contains the names and the current status of all documents. Possible states are
document unchanged
Pending
Processing …
Done
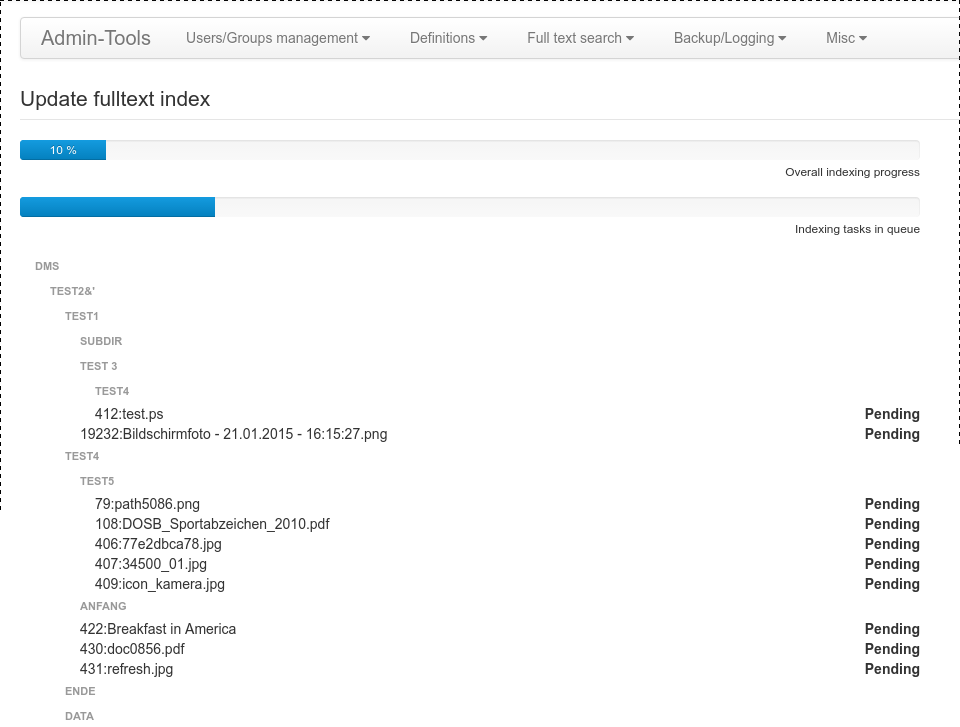
Creating the fulltext index
A document with status ‘document unchanged’ will not be indexed again, because it has not been updated since the last indexing. If a document needs to be updated in the index, it will first be in state ‘Pending’, when it is being indexed it has the state ‘Processing …’ and once that is ready, it will change to ‘Done’. The progress bars show the overall progress and the currently in parallel processed documents which may be 5 at most. The parallelization is done by the browser which retains a queue and spawns a new indexing progress if there is a free slot in the queue. If fulltext indexing is turned on, there will also be another item in the folder menu for indexing just that particular folder including all subfolders. This comes handy if a new document was just uploaded and shall be visible in the fulltext index without doing a full index update.
The admin tools contain besides updating and creating a fulltext index a third function to list the current data in the fulltext index. It is helpful to check whether the indexing is working at all. Once more documents are being indexed the page gets quite large and may take some to fully load. There are several sections on the page containing the terms which were indexed in the meta data fields and the content. The by far largest section is titled ‘content’. It lists all terms found in the document’s content.
Fulltext engine
SeedDMS supports two variants of fulltext indexes
Zend Lucene
SQLiteFS
Zend Lucene is available since version 3.2.0 of SeedDMS. SQLiteFS has been introduced in version 4.3.20. Both work well, thought SQLiteFS is faster and does not depend on the Zend Framework which is only part of the distribution because of the Zend Lucene fulltext engine. Hence, if you use SQLiteFS, you will not need the Zend Framework for SeedDMS anymore.
Commands for indexing
The fulltext index can only index plain text content and reads it from the standard output of a program. Hence, SeedDMS relies on external programs which do the conversion of arbitrary file formats and provide an utf-8 encoding output stream. Those commands need to be configured for each mimetype in the configuration of SeedDMS. The command may contain the placeholder %s which stands for the name of the file to be indexed. SeedDMS will fill in the name, call the external program and index the text written to standard out. This rather generic process allows to index almost any kind of file if appropriate software is available, e.g. even images or audio files if optical character recognition or speech recognition software is used.
The following list contains some common commands which can be used on a Linux/Unix system, if the required software is installed. If the programs are not installed within your search path, you might specify the complete path of the program.
- application/pdf
pdftotext -enc UTF-8 -nopgbrk %s - | sed -e ‘s/ [a-zA-Z0-9.] {1} / /g’ -e ‘s/[0-9.]//g’
This command filters out all words which contain only numbers and a period. If this is not desired (e.g. because the prevents indexing of invoice numbers), the second expression of sed should be removed.
- application/msword
catdoc ‘%s’
- application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document
docx2txt ‘%s’ -
- application/vnd.msexcel
xls2csv ‘%s’
- application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet
xlsx2csv ‘%s’
- all office formats
unoconv -d document -f text –stdout ‘%s’
This command is based on libre office and can handle most office formats. It maybe slower than using docx2txt, catdoc, xls2csv or xlsx2csv.
- audio/mp3, audio/mpeg
id3 -l -R ‘%s’ | egrep ‘(Title|Artist|Album)’ | sed ‘s/^[^:]*: //g’
- text/html
html2text ‘%s’
- text/plain, text/csv, application/csv
cat ‘%s’
Running the indexing task
Since version 6.0.x SeedDMS contains a scheduler with some predefined tasks. One of them is for updating or recreating the fulltext index. Please refer to the section `Scheduler`_ on how to setup a task.
A possible strategy for indexing could be to update the index hourly and recreate it once a day in the middle of the night.
Running the indexing script
The utils directory in the SeedDMS distribution also contains a script seeddms_indexer for indexing. Just run it with the command line parameter -h for help on using it. The script can be run manually once in a while but is usually called by a cronjob. In so far, it is very similar to the indexing task as described above, but without the scheduler in between. This script is also available for SeedDMS 5, while the scheduler task requires SeedDMS 6.